LONDON (AP) — A leading adviser to the World Health Organization described the unprecedented outbreak of the rare disease monkeypox in developed countries as “a random event” that might be explained by risky sexual behavior at two recent mass events in Europe.
In an interview with The Associated Press, Dr. David Heymann, who formerly headed WHO’s emergencies department, said the leading theory to explain the spread of the disease was sexual transmission among gay and bisexual men at two raves held in Spain and Belgium. Monkeypox has not previously triggered widespread outbreaks beyond Africa, where it is endemic in animals.
“We know monkeypox can spread when there is close contact with the lesions of someone who is infected, and it looks like sexual contact has now amplified that transmission,” said Heymann.
That marks a significant departure from the disease’s typical pattern of spread in central and western Africa, where people are mainly infected by animals like wild rodents and primates and outbreaks have not spilled across borders.
To date, WHO has recorded more than 90 cases of monkeypox in a dozen countries including Britain, Spain, Israel, France, Switzerland, the U.S. and Australia.
HOGP
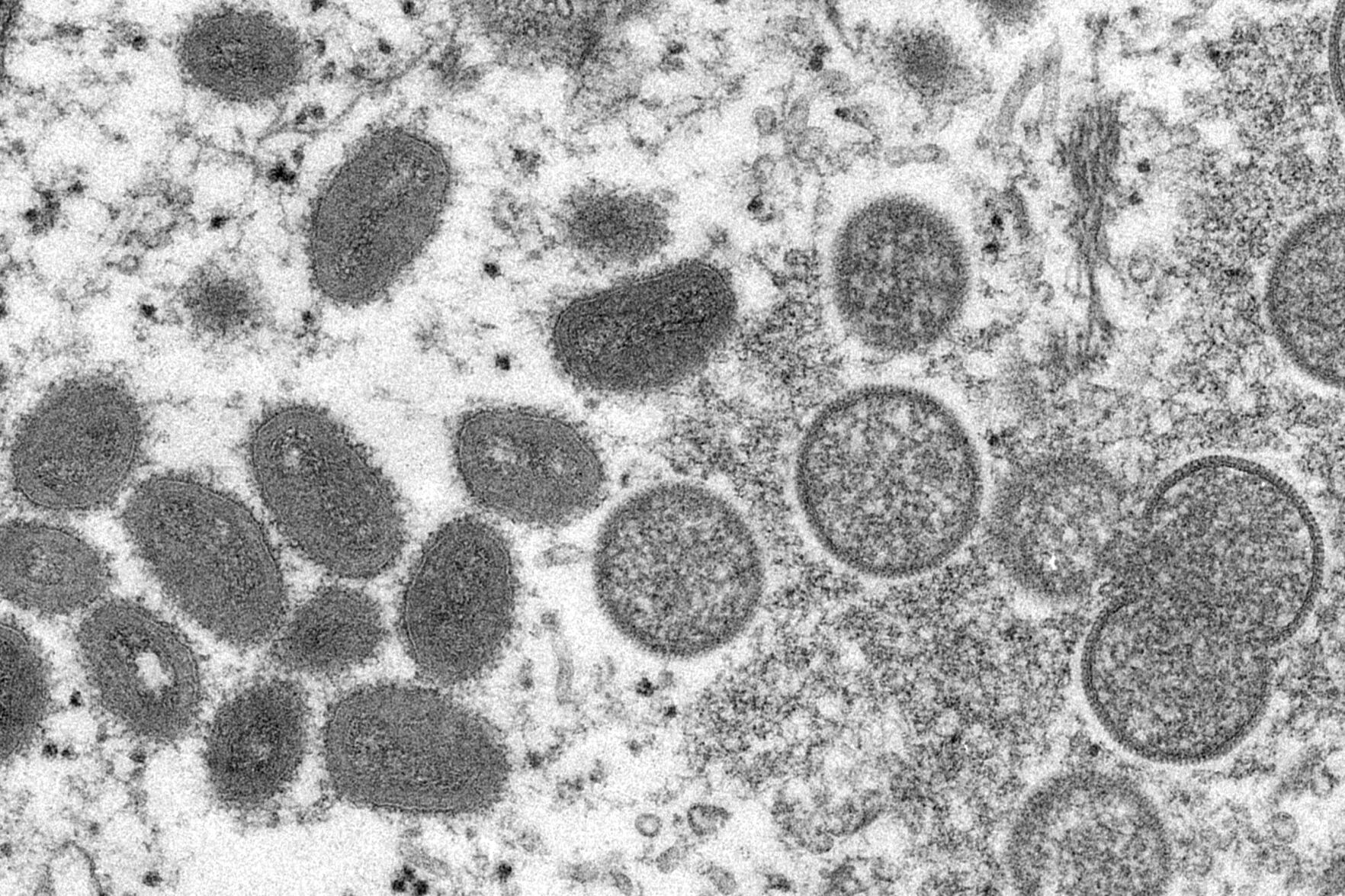
FILE - This 2003 electron microscope image made available by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows mature, oval-shaped monkeypox virions, left, and spherical immature virions, right, obtained from a sample of human skin associated with the 2003 prairie dog outbreak. A leading doctor who chairs a World Health Organization expert group described the unprecedented outbreak of the rare disease monkeypox in developed countries as "a random event" that might be explained by risky sexual behavior at two recent mass events in Europe. (Cynthia S. Goldsmith, Russell Regner/CDC via AP, File)
Madrid’s senior health official said on Monday that the Spanish capital has recorded 30 confirmed cases so far. Enrique Ruiz Escudero said authorities are investigating possible links between a recent Gay Pride event in the Canary Islands, which drew some 80,000 people, and cases at a Madrid sauna.
Heymann chaired an urgent meeting of WHO’s advisory group on infectious disease threats on Friday to assess the ongoing epidemic and said there was no evidence to suggest that monkeypox might have mutated into a more infectious form.
Monkeypox typically causes fever, chills, rash, and lesions on the face or genitals. It can be spread through close contact with an infected person or their clothing or bedsheets, but sexual transmission has not yet been documented. Most people recover from the disease within several weeks without requiring hospitalization. Vaccines against smallpox, a related disease, are also effective in preventing monkeypox and some antiviral drugs are being developed.
-
Expert: Monkeypox likely spread by sex at 2 raves in Europe
Cynthia S. Goldsmith, Russell Regner/CDC via AP
Monkeypox is a virus that originates in wild animals like rodents and primates, and occasionally jumps to people. Most human cases have been in central and west Africa, where the disease is endemic.
The illness was first identified by scientists in 1958 when there were two outbreaks of a “pox-like” disease in research monkeys — thus the name monkeypox. The first known human infection was in 1970, in a 9-year-old boy in a remote part of Congo.
Cynthia S. Goldsmith, Russell Regner/CDC via AP
Monkeypox is a virus that originates in wild animals like rodents and primates, and occasionally jumps to people. Most human cases have been in central and west Africa, where the disease is endemic.
The illness was first identified by scientists in 1958 when there were two outbreaks of a “pox-like” disease in research monkeys — thus the name monkeypox. The first known human infection was in 1970, in a 9-year-old boy in a remote part of Congo.
-
Expert: Monkeypox likely spread by sex at 2 raves in Europe
AP photo/Janet Hostetter
Monkeypox belongs to the same virus family as smallpox but causes milder symptoms.
Most patients experience only fever, body aches, chills and fatigue. People with more serious illness may develop a rash and lesions on the face and hands that can spread to other parts of the body.
The incubation period is from about five days to three weeks. Most people recover within about two to four weeks without needing to be hospitalized.
Monkeypox can be fatal for up to one in 10 people and is thought to be more severe in children.
People exposed to the virus are often given one of several smallpox vaccines, which have been shown to be effective against monkeypox. Anti-viral drugs are also being developed.
On Thursday, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control recommended all suspected cases be isolated and that high-risk contacts be offered the smallpox vaccine.
AP photo/Janet Hostetter
Monkeypox belongs to the same virus family as smallpox but causes milder symptoms.
Most patients experience only fever, body aches, chills and fatigue. People with more serious illness may develop a rash and lesions on the face and hands that can spread to other parts of the body.
The incubation period is from about five days to three weeks. Most people recover within about two to four weeks without needing to be hospitalized.
Monkeypox can be fatal for up to one in 10 people and is thought to be more severe in children.
People exposed to the virus are often given one of several smallpox vaccines, which have been shown to be effective against monkeypox. Anti-viral drugs are also being developed.
On Thursday, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control recommended all suspected cases be isolated and that high-risk contacts be offered the smallpox vaccine.
-
-
Expert: Monkeypox likely spread by sex at 2 raves in Europe
AP Photo/Anja Niedringhaus, File
The World Health Organization estimates there are thousands of monkeypox infections in about a dozen African countries every year. Most are in Congo, which reports about 6,000 cases annually, and Nigeria, with about 3,000 cases a year.
Patchy health monitoring systems mean many infected people are likely missed, experts say.
Isolated cases of monkeypox are occasionally spotted outside Africa, including in the U.S. and Britain. The cases are typically associated with travel to Africa or contact with animals from areas where the disease is more common.
In 2003, 47 people in six U.S. states had confirmed or probable cases. They caught the virus from pet prairie dogs that been housed near imported small mammals from Ghana.
AP Photo/Anja Niedringhaus, File
The World Health Organization estimates there are thousands of monkeypox infections in about a dozen African countries every year. Most are in Congo, which reports about 6,000 cases annually, and Nigeria, with about 3,000 cases a year.
Patchy health monitoring systems mean many infected people are likely missed, experts say.
Isolated cases of monkeypox are occasionally spotted outside Africa, including in the U.S. and Britain. The cases are typically associated with travel to Africa or contact with animals from areas where the disease is more common.
In 2003, 47 people in six U.S. states had confirmed or probable cases. They caught the virus from pet prairie dogs that been housed near imported small mammals from Ghana.
-
Expert: Monkeypox likely spread by sex at 2 raves in Europe
AP Photo/Allen Sullivan
It's the first time monkeypox appears to be spreading among people who didn't travel to Africa.
In Europe, infections have been reported in Britain, Italy, Portugal, Spain and Sweden. Most of the cases involve men who have had sex with men.
Britain's Health Security Agency said its cases are not all connected, suggesting that there are multiple chains of transmission happening.
The infections in Portugal were picked up at a sexual health clinic, where the men sought help for lesions on their genitals.
On Wednesday, U.S. officials reported one case of monkeypox in a man who had recently traveled to Canada, where authorities are investigating potential infections.
AP Photo/Allen Sullivan
It's the first time monkeypox appears to be spreading among people who didn't travel to Africa.
In Europe, infections have been reported in Britain, Italy, Portugal, Spain and Sweden. Most of the cases involve men who have had sex with men.
Britain's Health Security Agency said its cases are not all connected, suggesting that there are multiple chains of transmission happening.
The infections in Portugal were picked up at a sexual health clinic, where the men sought help for lesions on their genitals.
On Wednesday, U.S. officials reported one case of monkeypox in a man who had recently traveled to Canada, where authorities are investigating potential infections.
-
-
Expert: Monkeypox likely spread by sex at 2 raves in Europe
Cynthia S. Goldsmith, Russell Regner/CDC via AP
It's possible, but it's unclear at the moment.
Monkeypox has not previously been documented to have spread through sex, but it can be transmitted through close contact with infected people, their body fluids and their clothing or bedsheets.
Michael Skinner, a virologist at Imperial College London, said it's still too early to determine how the men in the U.K. were infected.
“By nature, sexual activity involves intimate contact, which one would expect to increase the likelihood of transmission, whatever a person’s sexual orientation and irrespective of the mode of transmission," Skinner said.
Francois Balloux of University College London said monkeypox said sex qualifies as the kind of close contact needed to transmit the disease.
The U.K. cases "do not necessarily imply any recent change in the virus’ route of transmission,” Balloux said.
___
Barry Hatton in Lisbon, Portugal, contributed to this report.
Cynthia S. Goldsmith, Russell Regner/CDC via AP
It's possible, but it's unclear at the moment.
Monkeypox has not previously been documented to have spread through sex, but it can be transmitted through close contact with infected people, their body fluids and their clothing or bedsheets.
Michael Skinner, a virologist at Imperial College London, said it's still too early to determine how the men in the U.K. were infected.
“By nature, sexual activity involves intimate contact, which one would expect to increase the likelihood of transmission, whatever a person’s sexual orientation and irrespective of the mode of transmission," Skinner said.
Francois Balloux of University College London said monkeypox said sex qualifies as the kind of close contact needed to transmit the disease.
The U.K. cases "do not necessarily imply any recent change in the virus’ route of transmission,” Balloux said.
___
Barry Hatton in Lisbon, Portugal, contributed to this report.
In recent years, the disease has been fatal in up to 6% of infections, but no deaths have been reported among the current cases. WHO said confirmed cases have so far been the less severe West African group of monkeypox viruses and appeared to be linked to a virus that was first detected in exported cases from Nigeria to Britain, Israel and Singapore in 2018-2019.
The U.N. agency said the outbreak is “a highly unusual event” and said the fact that cases are being seen in so many different countries suggests the disease may have been silently spreading for some time. The agency’s Europe director warned that as summer begins across the continent, mass gatherings, festivals and parties could accelerate the spread of monkeypox.
Other scientists have pointed out that it will be difficult to disentangle whether it is sex itself or the close contact related to sex that has driven the recent spread of monkeypox across Europe.
“By nature, sexual activity involves intimate contact, which one would expect to increase the likelihood of transmission, whatever a person’s sexual orientation and irrespective of the mode of transmission,” said Mike Skinner, a virologist at Imperial College London.
On Sunday, the chief medical adviser of Britain’s Health Security Agency, Dr. Susan Hopkins, said she expected more monkeypox cases to be identified in the country “on a daily basis.”
U.K. officials have said “a notable proportion” of the cases in Britain and Europe have been in young men with no history of travel to Africa and who are gay, bisexual or have sex with men. Authorities in Portugal and Spain also said their cases were in men who mostly had sex with other men and whose infections were picked up when they sought help for lesions at sexual health clinics.
Heymann, who is also a professor of infectious diseases at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, said the monkeypox outbreak was likely a random event that might be traceable to a single infection.
“It’s very possible there was somebody who got infected, developed lesions on the genitals, hands or somewhere else, and then spread it to others when there was sexual or close, physical contact,” Heymann hypothesized. “And then there were these international events that seeded the outbreak around the world, into the U.S. and other European countries.”
He emphasized that the disease was unlikely to trigger widespread transmission.
“This is not COVID,” he said. “We need to slow it down, but it does not spread in the air and we have vaccines to protect against it.” Heymann said studies should be conducted rapidly to determine if monkeypox could be spread by people without symptoms and that populations at risk of the disease should take precautions to protect themselves.

