
Getty Images
Rising prices (i.e., inflation) are everywhere you look — on the news, at the pump and in the grocery store. We notice these changes when we reach for our wallets, but it’s difficult to grasp what an extra dollar here or several dollars there mean over the course of several weeks, months or an entire year.
With prices up 8.5% year over year, household spending — that’s yours and mine — stands to rise by several thousand dollars. Even with the Federal Reserve’s attempts to control inflation through interest rate increases, it’s unlikely these prices will fall dramatically. This climb isn’t just a tank of gas or a few additional dollars at the store. For some people, it could be an entire paycheck every month.
Using inflation and annual spending data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, we looked at how spending in 2022 will differ from 2020, the last full year when inflation was relatively stable. We chose a handful of categories that many, if not most, Americans spend money on, such as food and electricity. The inflationary impact is remarkable.
Household expenditures could rise by $11,500
In all of 2020, American households spent $61,300, on average. This number includes everything we spend our money on: housing, food, entertainment, clothing, transportation and everything else. In 2022, it stands to reach $72,900, a difference of more than $11,500 if consumers want to maintain the same standard of living. Keep in mind, this is an average, a number that represents an approximation across all Americans, but one that’s exact to a very few. Those who earn (and therefore spend) more will see more dramatic dollar increases. Those who earn less may see less dramatic dollar jumps, but the impact of these rising prices could be more significantly felt.
It’s worth calling out — spending was a bit unusual in 2020. People spent less on commuting, child care and entertainment, for example, and more on home improvements. It’s a safe assumption that people will spend less in certain categories this year too, if for no other reason than avoiding high prices. This is primarily why we think spending in 2022 will be more similar to 2020 than 2019, for example, another year for which such spending data was available.
We can all likely agree that $11,500 is a lot more money to spend in a single year, but grasping what big numbers like that mean in practice can be difficult. Per month, you’re looking at close to $1,000 more. For many people, this is an entire extra rent or mortgage payment.
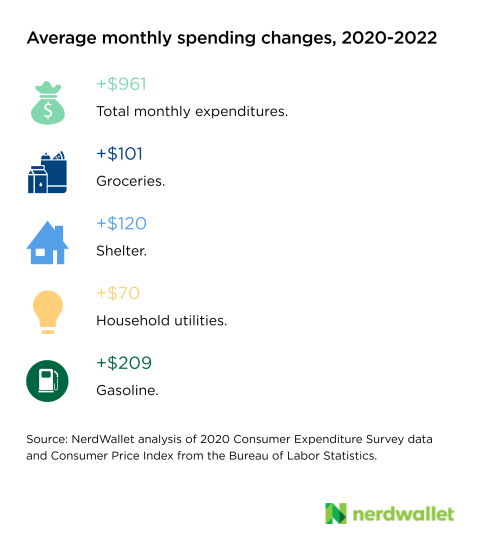
Across all the spending categories we examined, groceries, shelter and gas stand to rise the most. Throughout all of 2022, if inflation doesn’t slow considerably, we can expect to spend $1,200, $1,400 and $2,500 more on these categories, respectively.
Click here for a table of all anticipated spending changes.
How this situation plays into the recession conversation
The Fed is attempting to bring prices down gently. By raising the interest rate at which banks borrow money, it can control demand in the economy, and with cooler demand comes lower prices. However, these changes can also trigger not-so-great effects such as higher unemployment and slowing the economy too much. It’s a balancing act.
Though a recession may sound scary (and a deep one is), a downturn may be necessary to get prices under control. And as tough as it is to stomach, that part is a good thing.
How to handle high prices and recession talk
Look at the big picture
As explained above, there is a silver lining to an economic downturn or recession — prices fall. While the Fed attempts to achieve this outcome with a minimally negative impact, doomscrolling news websites and listening to overly simplified hot takes on social media will do absolutely nothing to protect you. Keep calm. Bolster your emergency savings if you’re able, see if you can tighten up your budget and sit back. Even when it comes to your long-term investments, sometimes the best advice is to relax and do nothing.
Expect to see the effects of rising rates
If you were planning on buying a house or a car in the near future, expect to pay far more for those items if you’re taking out a loan. Banks and creditors pass along their increased rates from the Fed to you, the consumer. Monthly payments will be bigger (perhaps by hundreds of dollars) due to the one-two punch of higher prices and higher interest.
Don’t forget about credit cards — interest rates will climb here too. Now more than ever, do your best to pay off your balances each month. The compounding interest of credit card debt is already high enough to try to avoid, when possible.
Budget more for necessary goods and services, temporarily
Revisiting your budget in the current climate doesn’t only involve cutting things out, but figuring out how to accommodate spending more in certain categories. After all, you can’t go without things like groceries. In order to maintain the same volume of groceries you had last year or the year prior, you’ll need to find the extra money. If you didn’t have much wiggle room in your budget to begin with, consider what items you can go without or cut back on. Maybe you can get another year out of that winter coat or cut out one or two streaming services. Framing these as temporary sacrifices makes losing them easier.
___
-
Most electric vehicles won’t qualify for federal tax credit
AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File
The biggest investment ever in the U.S. to fight climate change. A hard-fought cap on out-of-pocket prescription drug costs for Medicare recipients. A new corporate minimum tax to ensure big businesses pay their share.
And billions left over to pay down federal deficits.
All told, the Democrats' “Inflation Reduction Act” may not do much to immediately tame inflationary price hikes. But the package that won final congressional approval in the House on Friday and heading to the White House for President Joe Biden's signature will touch countless American lives with longtime party proposals.
Not as robust as Biden's initial ideas to rebuild America's public infrastructure and family support systems, the compromise of health care, climate change and deficit-reduction strategies is also a stunning election year turnaround, a smaller but not unsubstantial product brought back to political life after having collapsed last year.
Democrats alone support the package, with all Republicans voting against it Friday. Republicans deride the 730-page bill as big government overreach and point particular criticism at its $80 billion investment in the IRS to hire new employees and go after tax scofflaws.
Voters will be left to sort it out in the November elections, when control of Congress will be decided.
Here's what's in the estimated $740 billion package — made up of $440 billion in new spending and $300 billion toward easing deficits..
AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File
The biggest investment ever in the U.S. to fight climate change. A hard-fought cap on out-of-pocket prescription drug costs for Medicare recipients. A new corporate minimum tax to ensure big businesses pay their share.
And billions left over to pay down federal deficits.
All told, the Democrats' “Inflation Reduction Act” may not do much to immediately tame inflationary price hikes. But the package that won final congressional approval in the House on Friday and heading to the White House for President Joe Biden's signature will touch countless American lives with longtime party proposals.
Not as robust as Biden's initial ideas to rebuild America's public infrastructure and family support systems, the compromise of health care, climate change and deficit-reduction strategies is also a stunning election year turnaround, a smaller but not unsubstantial product brought back to political life after having collapsed last year.
Democrats alone support the package, with all Republicans voting against it Friday. Republicans deride the 730-page bill as big government overreach and point particular criticism at its $80 billion investment in the IRS to hire new employees and go after tax scofflaws.
Voters will be left to sort it out in the November elections, when control of Congress will be decided.
Here's what's in the estimated $740 billion package — made up of $440 billion in new spending and $300 billion toward easing deficits..
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
Launching a long-sought goal, the bill would allow the Medicare program to negotiate prescription drug prices with pharmaceutical companies, saving the federal government some $288 billion over the 10-year budget window.
Those new revenues would be put back into lower costs for seniors on medications, including a $2,000 out-of-pocket cap for older adults buying prescriptions from pharmacies.
Money would also be used to provide free vaccinations for seniors, who now are among the few not guaranteed free access, according to a summary document.
AP file
Launching a long-sought goal, the bill would allow the Medicare program to negotiate prescription drug prices with pharmaceutical companies, saving the federal government some $288 billion over the 10-year budget window.
Those new revenues would be put back into lower costs for seniors on medications, including a $2,000 out-of-pocket cap for older adults buying prescriptions from pharmacies.
Money would also be used to provide free vaccinations for seniors, who now are among the few not guaranteed free access, according to a summary document.
-
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
The bill would extend the subsidies provided during the COVID-19 pandemic to help some Americans who buy health insurance on their own.
Under earlier pandemic relief, the extra help was set to expire this year. But the bill would allow the assistance to keep going for three more years, lowering insurance premiums for people who are purchasing their own health care policies.
AP file
The bill would extend the subsidies provided during the COVID-19 pandemic to help some Americans who buy health insurance on their own.
Under earlier pandemic relief, the extra help was set to expire this year. But the bill would allow the assistance to keep going for three more years, lowering insurance premiums for people who are purchasing their own health care policies.
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
The bill would invest $369 billion over the decade in climate change-fighting strategies including investments in renewable energy production and tax rebates for consumers to buy new or used electric vehicles.
It's broken down to include $60 billion for a clean energy manufacturing tax credit and $30 billion for a production tax credit for wind and solar, seen as ways to boost and support the industries that can help curb the country's dependence on fossil fuels.
For consumers, there are tax breaks as incentives to go green. One is a 10-year consumer tax credit for renewable energy investments in wind and solar. There are tax breaks for buying electric vehicles, including a $4,000 tax credit for purchase of used electric vehicles and $7,500 for new ones.
In all, Democrats believe the strategy could put the country on a path to cut greenhouse gas emissions 40% by 2030, and "would represent the single biggest climate investment in U.S. history, by far."
AP file
The bill would invest $369 billion over the decade in climate change-fighting strategies including investments in renewable energy production and tax rebates for consumers to buy new or used electric vehicles.
It's broken down to include $60 billion for a clean energy manufacturing tax credit and $30 billion for a production tax credit for wind and solar, seen as ways to boost and support the industries that can help curb the country's dependence on fossil fuels.
For consumers, there are tax breaks as incentives to go green. One is a 10-year consumer tax credit for renewable energy investments in wind and solar. There are tax breaks for buying electric vehicles, including a $4,000 tax credit for purchase of used electric vehicles and $7,500 for new ones.
In all, Democrats believe the strategy could put the country on a path to cut greenhouse gas emissions 40% by 2030, and "would represent the single biggest climate investment in U.S. history, by far."
-
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
The biggest revenue-raiser in the bill is a new 15% minimum tax on corporations that earn more than $1 billion in annual profits.
It's a way to clamp down on some 200 U.S. companies that avoid paying the standard 21% corporate tax rate, including some that end up paying no taxes at all.
The new corporate minimum tax would kick in after the 2022 tax year and raise some $313 billion over the decade.
Money is also raised by boosting the IRS to go after tax cheats. The bill proposes an $80 billion investment in taxpayer services, enforcement and modernization, which is projected to raise $203 billion in new revenue — a net gain of $124 billion over the decade.
The bill sticks with Biden's original pledge not to raise taxes on families or businesses making less than $400,000 a year.
The lower drug prices for seniors are paid for with savings from Medicare's negotiations with the drug companies.
AP file
The biggest revenue-raiser in the bill is a new 15% minimum tax on corporations that earn more than $1 billion in annual profits.
It's a way to clamp down on some 200 U.S. companies that avoid paying the standard 21% corporate tax rate, including some that end up paying no taxes at all.
The new corporate minimum tax would kick in after the 2022 tax year and raise some $313 billion over the decade.
Money is also raised by boosting the IRS to go after tax cheats. The bill proposes an $80 billion investment in taxpayer services, enforcement and modernization, which is projected to raise $203 billion in new revenue — a net gain of $124 billion over the decade.
The bill sticks with Biden's original pledge not to raise taxes on families or businesses making less than $400,000 a year.
The lower drug prices for seniors are paid for with savings from Medicare's negotiations with the drug companies.
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
With $739 billion in new revenue and some $433 billion in new investments, the bill promises to put the difference toward deficit reduction.
Federal deficits have spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic when federal spending soared and tax revenues fell as the nation's economy churned through shutdowns, closed offices and other massive changes.
The nation has seen deficits rise and fall in recent years. But overall federal budgeting is on an unsustainable path, according to the Congressional Budget Office, which put out a new report this week on long-term projections.
AP file
With $739 billion in new revenue and some $433 billion in new investments, the bill promises to put the difference toward deficit reduction.
Federal deficits have spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic when federal spending soared and tax revenues fell as the nation's economy churned through shutdowns, closed offices and other massive changes.
The nation has seen deficits rise and fall in recent years. But overall federal budgeting is on an unsustainable path, according to the Congressional Budget Office, which put out a new report this week on long-term projections.
-
-
Senate deal should make it easier to buy electric vehicles
AP file
This latest package after 18 months of start-stop negotiations leaves behind many of Biden's more ambitious goals.
While Congress did pass a $1 trillion bipartisan infrastructure bill of highway, broadband and other investments that Biden signed into law last year, the president's and the party's other priorities have slipped away.
Among them, a continuation of a $300 monthly child tax credit that was sending money directly to families during the pandemic and is believed to have widely reduced child poverty.
Also gone, for now, are plans for free pre-kindergarten and free community college, as well as the nation's first paid family leave program that would have provided up to $4,000 a month for births, deaths and other pivotal needs.
Associated Press writer Matthew Daly contributed to this report.
AP file
This latest package after 18 months of start-stop negotiations leaves behind many of Biden's more ambitious goals.
While Congress did pass a $1 trillion bipartisan infrastructure bill of highway, broadband and other investments that Biden signed into law last year, the president's and the party's other priorities have slipped away.
Among them, a continuation of a $300 monthly child tax credit that was sending money directly to families during the pandemic and is believed to have widely reduced child poverty.
Also gone, for now, are plans for free pre-kindergarten and free community college, as well as the nation's first paid family leave program that would have provided up to $4,000 a month for births, deaths and other pivotal needs.
Associated Press writer Matthew Daly contributed to this report.


